Optimizing RAN power consumption
Energy efficiency for mobile networks
Cost optimization and commitments to net zero have made energy efficiency a strategic priority for mobile network operators. In a 2023 GSMA Intelligence survey, operators ranked sustainability as the most important area of network transformation.
On average, energy usage accounts for 20-40% of operational expenditure (OpEx) for mobile network operators, despite continued efficiency improvements. Cost optimization is an urgent issue in the low revenue growth environment of telecommunications, especially with the continued pressure from new 5G builds on network capital expenditures (CapEx). Removing 5-10% from the energy OpEx would improve cashflow by 2-3 percentage points - even with no change in revenue growth. Sustainability is also a high priority for consumers, with 30-60% of telecommunications customers claiming that they would pay a premium for mobile tariffs that are carbon neutral.
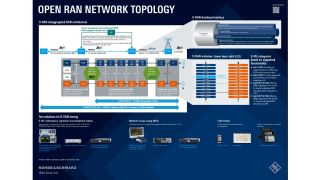
The radio access network (RAN) accounts for majority of the energy consumed by a typical mobile telecommunications system, and radio units (O-RU) are the most significant factor in total power consumption. RAN energy consumption includes BTS, Node B, eNodeB and gNodeB energy usage as well as the energy used by associated infrastructure, such as air conditioning, inverters and rectifiers. It also includes the energy used by repeaters and all energy consumption associated with backhaul transport.