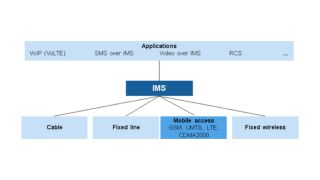
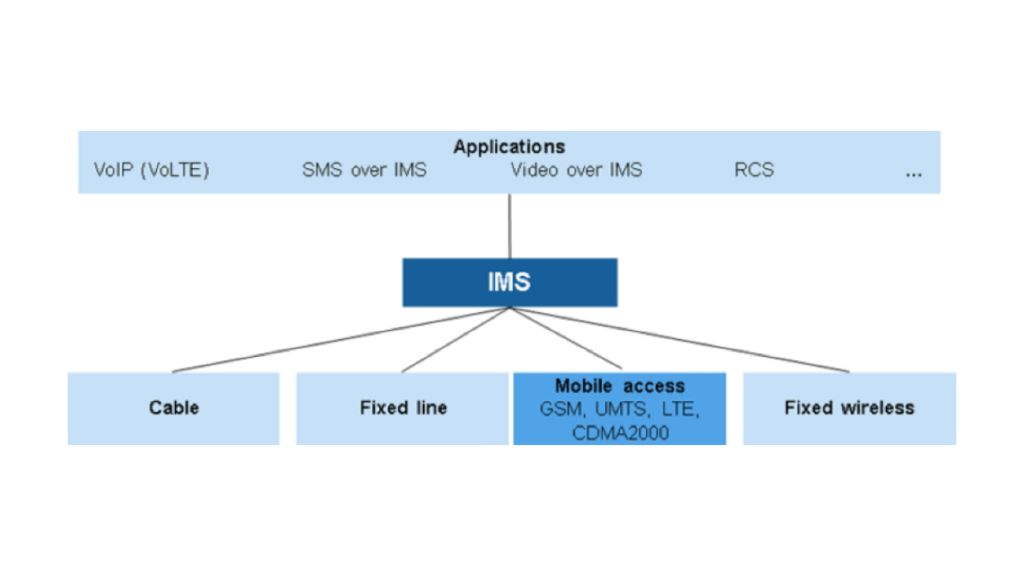
As cellular technology moves to LTE, it also has to move to an IP-based system. The Internet protocol multimedia subsystem (IMS) has been created as the long-term solution for covering voice over LTE (VoLTE) and connecting circuit-switched and packet-switched calls.
The IMS was developed in order to exploit the capabilities of modern IP-based mobile devices. These devices usually offer large displays, cameras and other resources that can be utilized by applications that not only exchange information with the user interface, but also strive to establish peer-to-peer (P2P) connections with other devices.
Conferencing, shared browsing and presence services are examples of such applications. Future applications that integrate voice and data services will require an architecture that is able to combine the offered mobility with the IP network.
The IMS is the architecture that provides this functionality.
The following features are supported:
- IP connectivity: the main requirement for IMS connectivity; the IMS therefore supports the use of radio access networks (RAN) as well as the use of non-RANs such as WLAN and DSL
- Negotiation of QoS requirements and capabilities between UEs
- IP policy control: authorizes usage and the amount of bearer traffic for IMS media
- Authentication schemes: ensure secure communications
- Charging arrangements: allow operators to charge end users on a situation-dependent basis, e.g. according to both parties' bearer usage, or based on the media components used
- Roaming
- Communications with PSTN, ISDN, mobile and Internet users as well as Internet applications
- Home service control only: the entity with access to the subscriber database, which interacts with the service platforms, is always located in the home network
- Service framework: provides capabilities to support speech, video, multimedia, messaging, file sharing, data transfer, gaming and basic supplementary services
- Layered design: separates transport and bearer services from the IMS signaling network; applications run on top
The IMS is an all-IP service layer between the transport and the application layers, and is based on common Internet protocols. It defines an architecture for the convergence of audio, video and data and will enable integrated multimedia sessions over fixed and wireless networks. While the focus in the initial stage of LTE networks will be on enabling voice and SMS over LTE, many more applications will need to be supported.