Analyze passive low frequency components
With a Rohde & Schwarz oscilloscope

With a Rohde & Schwarz oscilloscope
Vector network analyzers are perfect for analyzing passive or active components, such as filters, amplifiers, mixers and multiport modules. However, low frequency componentdesigners’ requirements include lower start frequencies – sometimes even down to a few Hertz. Traditional network analyzers usually have start frequencies in the kHz range.
Easily and quickly analyze low frequency response on your oscilloscope with the R&S®RTx-K36 frequency response analysis (Bode plot) option. Characterize the frequency response of a variety of electronics, including passive filters and amplifier circuits. The R&S®RTx-K36 frequency response analysis (Bode plot) option uses the oscilloscope’s built-in waveform generator to create stimulus signals ranging from 10 Hz to 25 MHz. Measuring the ratio of the stimulus signal and the output signal of the DUT at each test frequency, the oscilloscope plots gain and phase logarithmically.
The frequency response of RF networks is defined as the ratio between the output signal (termed as B wave) over the injected signal (termed as A wave).
Measuring the frequency response of a network requires a source generating signals across certain frequencies. The amplitude and phase of the input signal as well as at the output of the DUT must be measured for the calculation.
Use the Bode plot application to turn your Rohde & Schwarz oscilloscope into a frequency response analyzer.
Device setup
Connect the oscilloscope’s generator and one oscilloscope channel to the DUT input, and another oscilloscope channel to the DUT output.


Start the application:
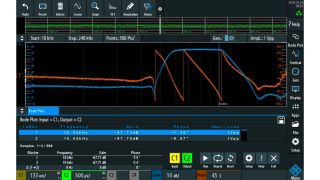
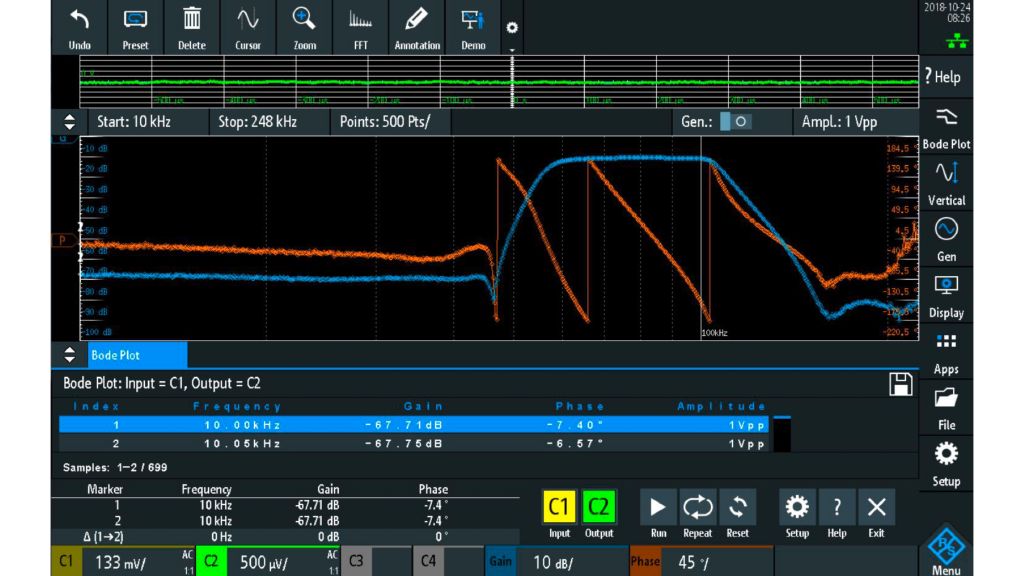
Measurement results
Gain and phase waveforms displayed in the Bode plots represent the transmission function of the DUT. Gain shows the amplitude frequency response frequency range in dB. The phase waveform displays the phase characteristics over frequency, measured in degrees.
Drag markers to the desired positions directly on the plotted trace. A legend displays the coordinates of the markers. To determine the cutoff frequency of a low pass filter, activate two markers. The cutoff frequency is defined as the frequency for which the output of the circuit is 3 dB below the nominal passband value.
Engineers use oscilloscopes as a primary measurement tool. Equip your oscilloscope with a Bode analysis option to determine the frequency response of passive components.
The R&S®RTx-K36 frequency response analysis (Bode plot) option for the R&S®RTB2000, R&S®RTM3000 and R&S®RTA4000 oscilloscopes provides a low-cost alternative to low frequency network analyzers or dedicated standalone frequency analyzers. With their 10-bit ADC, low noise and 25 MHz generator, the R&S®RTB2000, R&S®RTM3000 and R&S®RTA4000 oscilloscopes ideally meet the high dynamic range requirements of this measurement task.