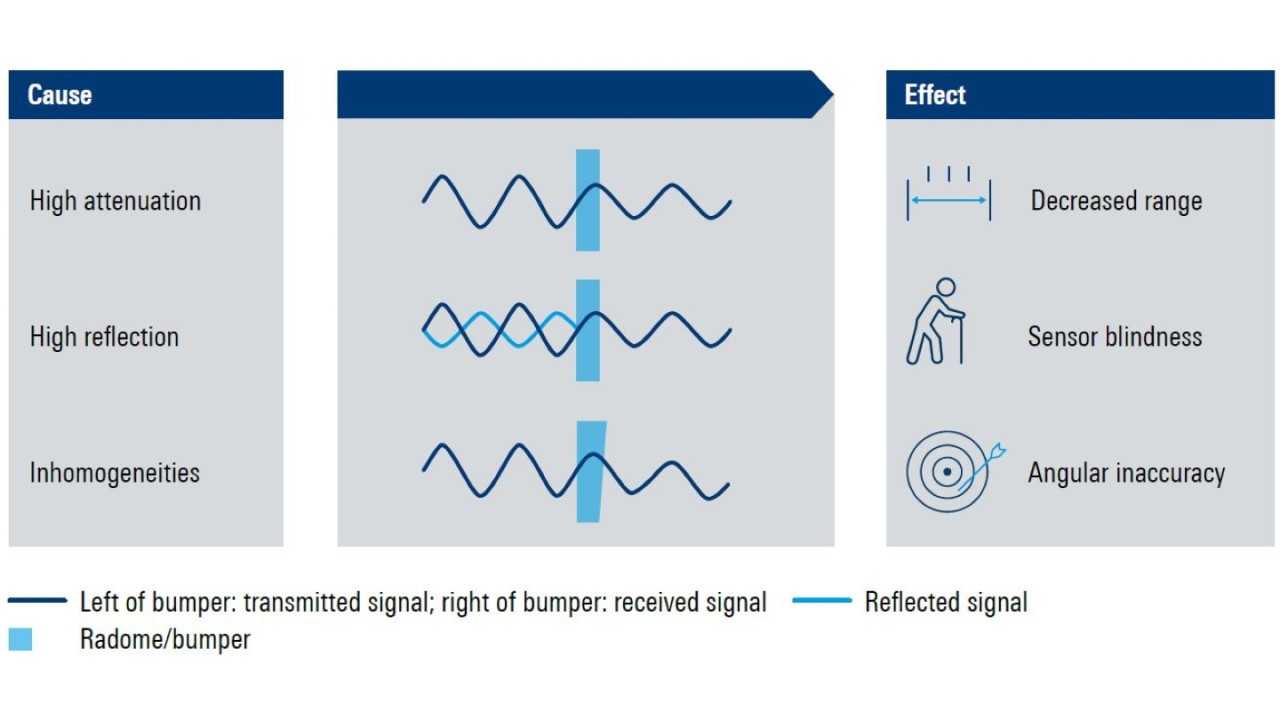
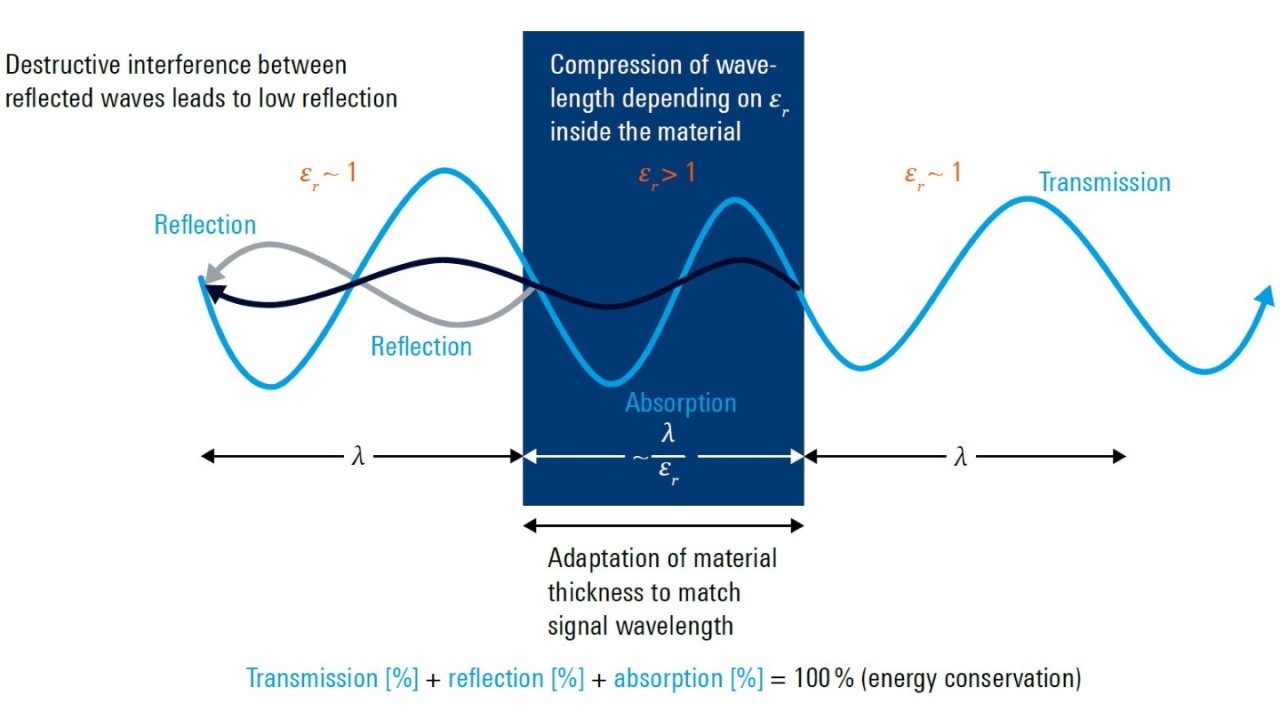
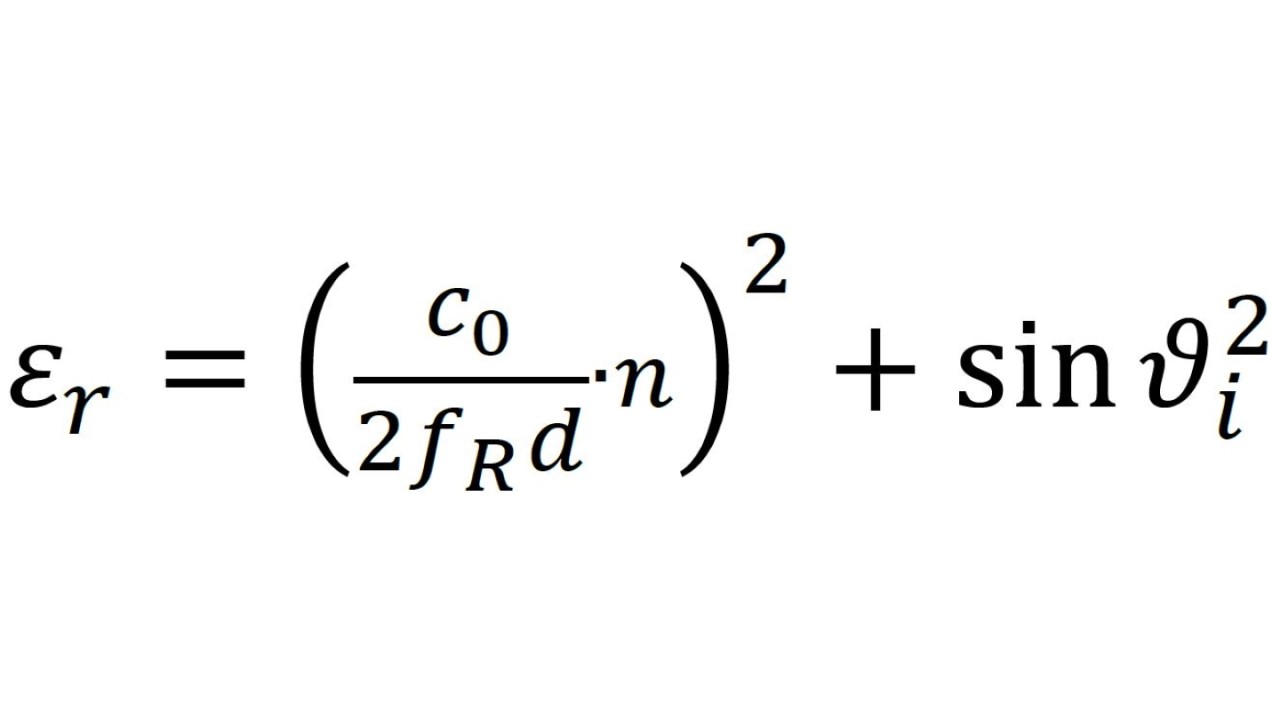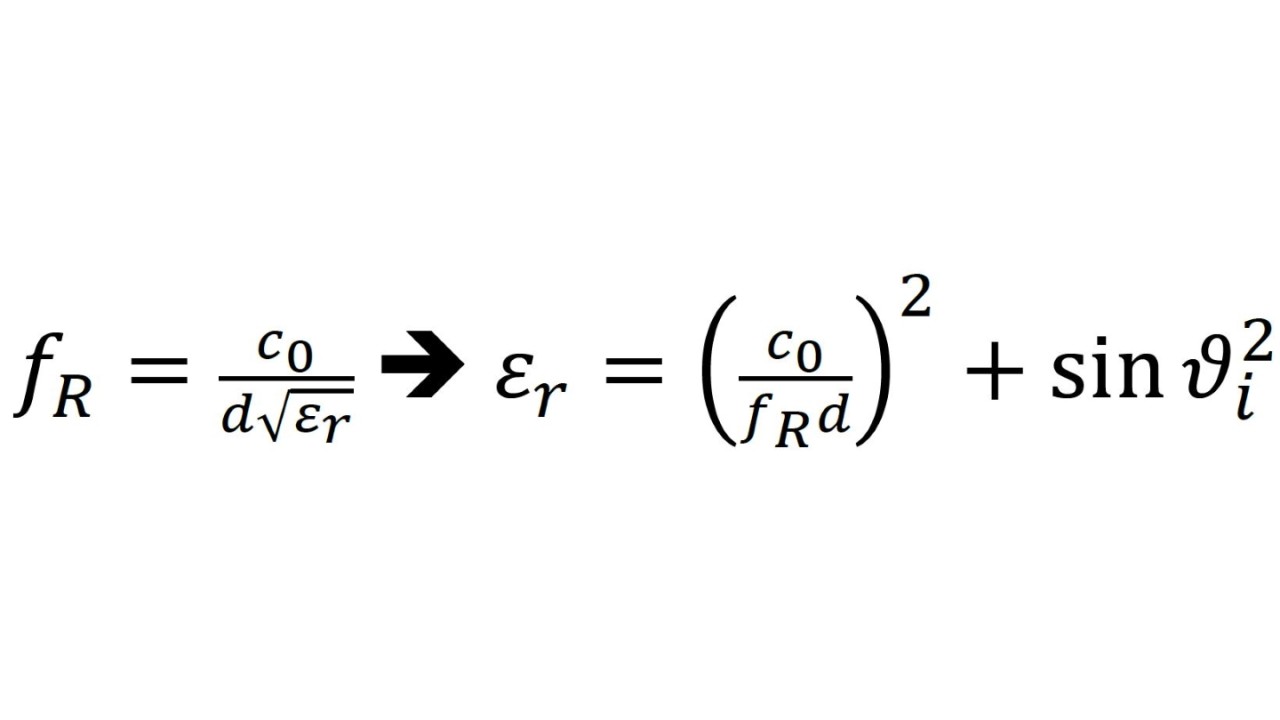Since all of these steps need to be repeated in quick succession, a simple measurement method is required that delivers robust and reliable results. Here, using RF signals to perform material measurements has a number of important advantages. First, and perhaps most importantly, this approach allows for nondestructive material testing. In many cases, we would like to obtain information about a material without destroying it in the process. Another important advantage is that RF signals allow material measurements to be made while the material is undergoing various physical, mechanical, thermal or chemical changes. The approach using RF signals to make material measurements focuses on determining the relative permittivity of a material.
One way of obtaining the relative permittivity is using a vector network analyzer (VNA). The VNA measures transmission and reflection as described in the following. For further details, refer to the document referenced on page 5 of this application card.
One approach taken for nondestructive testing is the freespace method as it is suitable for the 76 GHz high frequency radar band. This requires the VNA system, including a calibration kit, to work in that frequency range. The setup is complex and requires detailed VNA knowledge to achieve accurate and reproducible results. Vector network analyzers perform measurements at selected points, which means that the slightest deviation in angle has a massive effect on measurement values. Another limitation is that material samples need to be relatively large and flat in order to be properly illuminated by the antennas.