Your task
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) plans to extend positioning capabilities with a new channel sounding feature. The feature will be added along with advertising, RSSI-ranging and direction finding (DF) capabilities. Bluetooth® channel sounding (CS) will enable high accuracy distance measurements (HADM) between two Bluetooth® Low Energy devices. CS uses the relative phase shift between received and transmitted radio signals over multiple RF frequencies or the round trip time, based on packets or a combination of both. Typical HADM applications include keyless entry systems, indoor navigation and asset tracking with new use cases continuously being developed for future applications
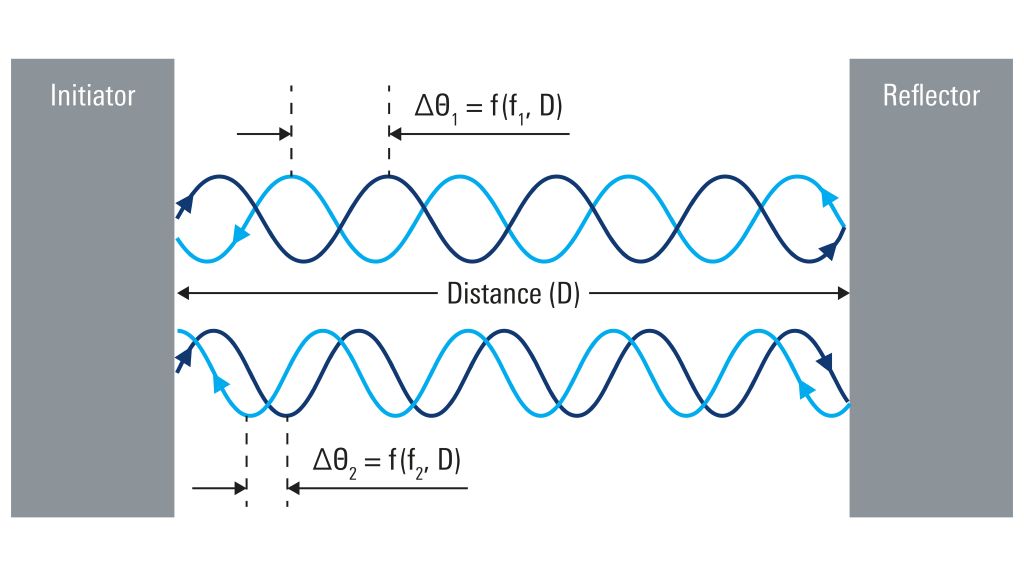
Phase based measurement principle
PBR uses the phase shift (Θ) of a radio signal as it travels over distance D at frequency f. When two or more signals with different frequencies are used, the measured phase difference (ΔΘ) between the signals can help accurately estimate a distance. When estimating a distance with channel sounding, one device initiates (initiator) the procedure and a second device reciprocates the radio transmission (reflector) without modifying the phase. For every transmission in the frequency f, the phase change (ΔΘi) between the transmitted and the received signal is measured by the initiator. Uncoded narrowband Gaussian minimum shift keying (GFSK) signals can be sent or received using a single antenna for easy implementation in standard Bluetooth® Low Energy radio chips. Alternatively, multiple antennas can be used to improve performance or DF coexistence.
Ensuring best in class accuracy
The Bluetooth SIG defined RFPHY test cases (TCs) to verify satisfactory device RF performance when a Bluetooth® DUT acts either as an initiator or reflector. Test solutions must operate both roles. Measurements must show that an initiator can generate the CS packets and tones with the required phase stability, that the reflector transmits signals with the correct phase and that general DUT phase measurements are accurate. The frequency offset also needs to be within a certain limit. When an antenna array is used, the antenna switching function must also be verified.